| Added | Fri, 06/01/2017 |
| Источники | |
| Феномены | |
| Версии |
It is considered that the term "UFOlogy" appeared in English in 1959. In particular, the Oxford English Dictionary reports the first use in the Times Literary Supplement 23 January 1959. It is known, however, that this article appeared eight years later, after Edward j. Ruppelt was first proposed and started to use the term UFO in 1951. The very beginning of UFOlogy, as the direction that studies unidentified flying objects began in the late 40-ies of XX century, when in 1947 K. Arnold saw nine strange flying objects, moving with inconceivable then supersonic speed (this event is known as "Case in the Cascade mountains").
However, despite the fact that the UFOlogy – direction, it is considered that the appearance of UFOs on Earth began long before 1947. To do this, to themselves as ufologists lead to various eyewitness accounts, sketches and photographs. Experts in the field of photography, astronomy, psychology, military equipment, aircraft, etc. can figure out where lies a grain of truth, but where outright falsification. And the rest need to have at least a General idea about these areas to be able to form an independent opinion.
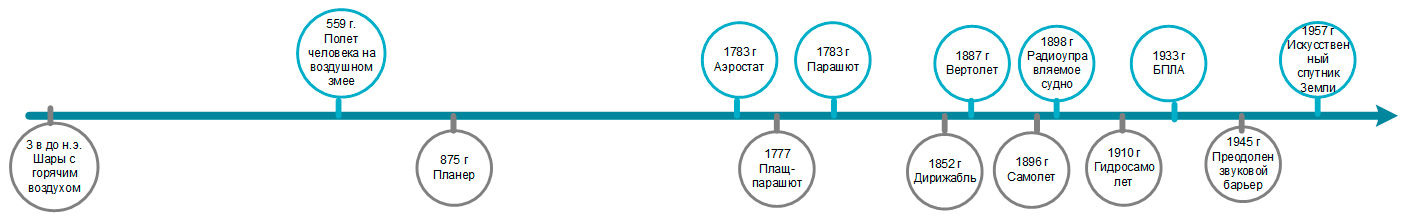
In this article we will talk about the history of Aeronautics: on the evolution and chronology of the advent of aircraft.
World history of Aeronautics
Since ancient times man has sought in the sky. There were many stories, myths and legends about the various aircraft: chariots of the gods, a magic carpet, wings that you can wear to fly like a bird, and much more. People have tried to come up with various devices that would allow them to fly.
The history of Aeronautics
Balloon
Flying lantern (a prototype of balloons with the envelope filled with hot air) has been known in China since ancient times. Its invention is attributed to the General Zhuge Liang (180-234 ad, honorific title Kunmin), which, according to the sources, used them to instill fear in the enemy troops.
However, according to some sources, it is considered that in the III century BC in China, were familiar with the device, which is a lamp in a paper container and resembled balloons with hot air.
In the V century BC Lu Ban invented the "wooden bird" that may have been a large kite or an early glider. However, there is no evidence that similar designs were used for human flight.
559 human flight on the kite has been documented in the Kingdom of Northern Wei.
Balloon
The first balloon of the Montgolfier brothers filled with hot air, climbed on 5 June 1783 in Annonay, and the second, built by Professor Charles and hydrogenated, up 27 Aug 1783, paving the way for the implementation of the present Aeronautics.
Balloons and dirigibles: 1-the Montgolfier Balloon, 2 Balloon, Charles, 3-Balloon Blanchard, a 4-Balloon (bal. captif) Giffard, 5 - Aerostat (free) Giffard, 6-Balloon Dupuy de Scrap, 7-Balloon Henlein, 8-the Balloon of Renard and Krebs
Further, aerostructure developed, increasing the lifting height, flight distance, as well as the variety of shapes and designs.
After the war of 1870-71. all aeronautic society, especially in Paris, with great zeal began searching for ways to control the balloon to make it suitable for practical purposes. The first rational attempt in this direction was made earlier, in 1852, Henri Giffard, built a cigar-shaped bowl shape, with a length of 44 meters and a diameter of 12 m, provided with screw drives the rotation of the steam machine.
The airship
The airship is essentially controlled balloon.
The Dirigible Santos-Dumont No. 6 [2]
The first airship was made in the form of an ellipsoid. It made its first flight only on 24 September 1852. Since the design is strongly developed, and in 1909 a Zeppelin (by the name of Ferdinand Zeppelin) was acquired by the military. In the future airships will play a significant role in the world wars of the twentieth century.
Parachute
The device, which was the prototype of the modern parachute was invented by the Arab scholar and inventor Abbas Ibn Farnas in 852 He made wings made of fabric stretched over wooden struts. This is similar to the umbrella apparatus of Abbas Ibn Farnas jumped from the minaret of the great Mosque in Cordoba.
The person about whom it is known that he made a descent by parachute was a Frenchman Laven. In 20-ies of the 17th century Laven was imprisoned in the fortress. Determined to escape, he secretly made himself a parachute from sheets sewn together with attached baleen, not giving dome to curl up.
Modern round parachute [10]
In 1777, Paris Professor Devontae invented the "flying Cape" - the device which, according to him, ensured a safe descent from any height.
The fate of the parachuting is associated with the development of Aeronautics. In 1783, French physicist Sebastien Lenormand made and personally tested the parachute by jumping from the Observatory. Lenormand called his invention - the "parachute".
In 1791 Jean-Pierre Blanchard rose in the air above the town and dropped by parachute dog. Two years later he ventured to make the jump. The attempt was not entirely successful - aeronaut broke his leg.
The first successful parachute jump from the basket of the balloon was made in Paris in 1797, Andre Jacques Gameroom with balloon rose to a height of 680 meters. His parachute (round, soft, without a frame, with a pole hole) very close to the most prevailing type of modern parachute is an umbrella.
A kind of milestone in the history of the parachute case was the jump, the perfect American captain Erwin Baldwin, with the balloon in 1880.
The principle of operation of a parachute [3]
It is interesting in that the chute opened automatically. To the upper node of the sling was attached the line cord, the second end of which is fixed on the basket or the balloon. When the parachute separated from the balloon, the line-cord under his weight broke, fabric dome without any frame speed drop is first stretched at full length, and then inflated and unfolded.
This principle of automatic parachute deployment has been preserved to our days. During the 19th century chute has improved, but significant changes in technology were not. [3]
Experimental aircraft
At different times there were a huge number of experimental aircraft with different shapes and characteristics. They were required to conduct experimental design, experimental, research works, and also test (and transport testing) aviation, space, nuclear and other equipment.
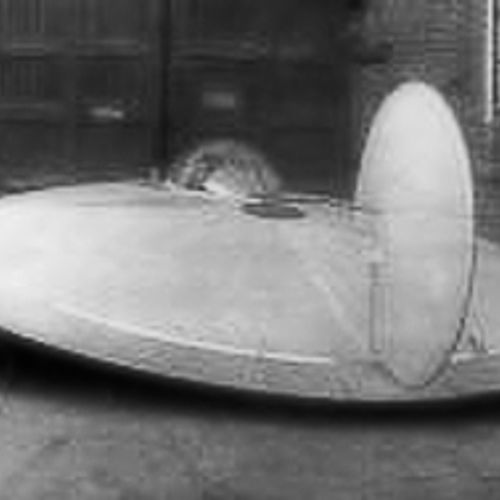
As example, Diskoplan. In 1950, under the leadership of Sukhanov by Novosibirsk group of designers was developed and built airframe "Diskoplan-1".
Diskoplan-2 [5]
This glider has an interesting feature: when planning the height on landing, the pilot feels that diskoplan as if sits on a "pillow" and automatically stabiliziruemost in the transverse and longitudinal directions. Then the unit can fly without the intervention of the pilot in control. And you can't force the glider to accelerate the landing until the flight speed is naturally not extinguish the effect of the "cushion" will not disappear. After that, diskoplan will land yourself three points.
World history of the aircraft
Together with the development of lighter-than-air attempts were made in the construction of aircraft.
In the beginning was a structure resembling a kite. He was allowed to hang in the air, but was not allowed to fly and control the flight. Shortly people did it – was invented the glider.
The glider (hang glider)
Image of the first glider refer to the beginning of our era. During archaeological excavations in the desert, located in Peru, was discovered drawing unusual shapes called "parnassim chandelier". Specialists aviators have no doubt that this drawing of the aircraft, resembling a glider. Nearby was found a landing pad with the "landing strip" and an image reminiscent of "the wind rose".
875 g. Arab Ben Firans jumped off the roof of the house. To 1003. a similar attempt was made by al-Jauhari. Both flights failed - inventors received severe injuries.
Photo modern glider [4]
The first documented flight of a European refers to the eleventh century. In 1020 g. English Benedictine monk Aylmer of Malmesbury, called the monk, put on wings and jumped from the monastery bell tower.
In Russia in 1669 Sagittarius Ivan Sickles made "wings like a pigeon, but much larger". In the city of Ryazhsk he "wanted to fly, but only up yards on seven (i.e., about five meters), not the one who went in the air and fell to the ground."
In 1695, somebody went to the king with a request to give him money to create flying contraptions. From the Treasury he was selected to 18 cents, and the master started to work. In the course went sticks, mica, leather. Unfortunately, on the fate of the inventor is not known.
The plane
Official sources say that on may 6, 1896 "the Langley Aerodrome number 5" made the first successful flight of an unmanaged marker apparatus heavier than air to the engine.
Following the principle of Lilienthal jump before the flight, the Wright brothers built and tested a series of kites and gliders from 1900 to 1902 before to build a machine with the engine. The gliders flew successfully, but not as Wright expected, on the basis of experiments and letters to their predecessors of the nineteenth century. According to the Smithsonian Institute and the FAI Wright made the first controlled flight of a long machine heavier than air with the engines in sand dunes, 8 km from kitty hawk, North Carolina December 17 1903
Next aircraft design was improved and the next breakthrough in aircraft engineering was the development of the jet engine, which began in the 1930s in Germany and in England.
First practically applied by a jet aircraft was the Heinkel He 178 (Germany), made the first flight in 1939 (a Coanda-1910 at the message made the first unintentional short flight on 16 December 1910).
In October 1947, Charles Yeager on the plane, the rocket Bell X-1 (rocket engine) exceeded the sound barrier (although there is evidence that some fighter pilots may have exceeded the speed of sound during the war in the process of bombing in a dive, it was the first controlled flight, during which was recorded the excess of the speed of sound).
Helicopter
In 1877 Enrico Forlanini created an unmanned helicopter with a steam engine. He rose to a height of 13 metres, where I remained for about 20 seconds, vertically taking off in a Park in Milan.
The first piloted helicopter which rose above the ground, was designed Field the Root. This flight took place in 1907, but the first practical helicopter was the Focke FA-61 (Germany, 1936). He was the first flying machine that lifted off the ground using a rotating blade instead of wings.
Seaplane
The first seaplane was built in March 1910 the French engineer Henri Fabre, please. He took off from the water and flew 800 meters during the first flight on 28 March 1910.
Unmanned aerial vehicles
At the beginning of the XXI century, in the development of subsonic aircraft the tendency for creation of remotely operated or completely Autonomous vehicles.
Distinguish unmanned aerial vehicles:
- unmanned unmanaged;
- unmanned automatic;
- unmanned remotely-piloted vehicles (RPV).
In 1898, Nikola Tesla developed and demonstrated miniature RC ship.
In 1910, inspired by the success of the Wright brothers, a young American army engineer from Ohio Charles Kettering suggested to use the aircraft without a human. According to his plan-driven clockwork device in a given place was supposed to drop wings and fall like a bomb on the enemy. With funding of the U.S. army, he built and with varying success has tested a few devices, but in the fighting they have not been applied.
In 1933 in the UK developed the first UAV reusable Queen Bee.
In the future, the design of the UAV modernized and was modified depending on the purpose.
The conquest of space
This section is included in this article to show, when the sky became possible to notice the "uniformly moving star" that is actually an artificial satellite of the Earth.
In 1949, the idea of launching into space of rockets for research purposes began to be realized. Geophysical devices taking off to a height of 100-200 and then 400 km, paved the way for satellites.
November 4, 1957 with the secret "site No. 2" was successfully launched the rocket with the satellites. Sputnik was simply a metal sphere with a radio transmitter inside. Scientific laboratory, weighing more than a ton, flew for the atmosphere only at the third satellite on 15 may 1958
In 1962, she adopted a multi-purpose program "Cosmos", which was carried out satellite launches conducted in both peacetime and military purposes.
In November 1957, the second satellite went into space dog Laika, who became the first "living space" of the Earth. [8]
Then followed a whole series of runs with the animals, which allowed us to send a man into space Yuri Gagarin. The launch of the spacecraft "Vostok-1" was produced April 12, 1961 at 09:07 Moscow time from the Baikonur cosmodrome. [9]
Conclusion
Thus, we can conclude that various aircraft began to appear in the sky very long time, and for most of the population, they were really unrecognized because of the limitations of knowledge. You cannot say that all the evidence of strange technical devices in the sky to the 19th century is the direct evidence for the alien theory.
Based on the above information one can make conclusions for themselves regarding certain historical accounts, drawings and photographs, offered by some as evidence of the ancient history of UFOs.
Experts in the field of aviation are invited to write a review article about an interesting model of experimental aircraft that could be mistaken for UFOs.
As a more detailed source of information you can recommend a website Aviaschool.net devoted to aviation and Aeronautics, and welcome "corner of the sky".
Translated by «Yandex.Translator»
Log in or register to post comments