| Added | Tue, 30/05/2023 |
| Источники | |
| Дата публикации | Thu, 25/05/2023
|
| Версии |
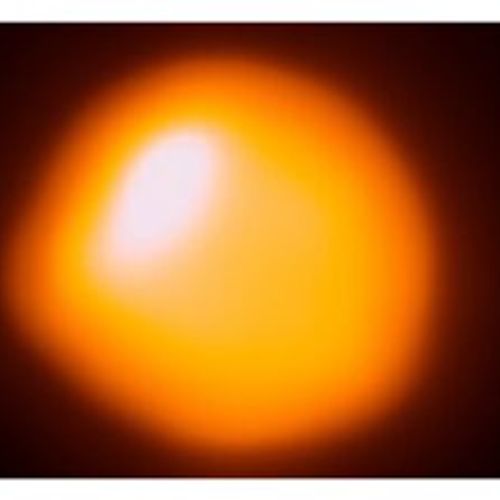
Betelgeuse, a red giant on the verge of death, continues to show unusual behavior. After the Great Blackout that occurred in late 2019 and early 2020, the star became unusually bright. It is currently the seventh brightest star in the sky, while it usually ranks tenth. This has led to speculation that Betelgeuse is preparing to explode in an exciting supernova.
However, scientists believe that it is too early to talk about this and probably this behavior is due to ongoing fluctuations after the Great Blackout of 2019, and the star will return to normal within a decade.
Betelgeuse is one of the most interesting stars in the sky. It is located at a distance of about 700 light-years from Earth and is a red giant in the last stage of its life. It is also an unusual star for a red giant because it was previously a monster - a blue-white O-type star, the most massive class of stars.
Betelgeuse has changed its spectral type because it has almost exhausted its hydrogen reserves. Now it burns helium into carbon and oxygen and has expanded to gigantic proportions: about 764 times the size of the Sun and about 16.5-19 times its mass.
Eventually, it will run out of fuel to burn, become a supernova, throw out its outer material, and its core will collapse into a neutron star.
Before the Great Blackout, Betelgeuse also had periodic brightness fluctuations. The longest of these cycles is about 5.9 years, and the other is 400 days. But it seems that the Great Blackout caused a change in these fluctuations.
A new paper prepared by astrophysicist Morgan McLeod from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics has shown that the 400-day cycle seems to have halved. This pulsation cycle is probably caused by expansion and contraction inside the star. According to simulations conducted by McLeod and his colleagues, the convective flow inside Betelgeuse could rise and become a material that separates from the star.
Новости со схожими версиями
Log in or register to post comments